
Sometimes referred to as “smart automation” or “intelligent automation,” “RPA” is an umbrella term for advanced software systems that can be programmed to perform a series of tasks that previously required human intervention.
Other robotic solutions incorporate machine learning and include cognitive computing and artificial intelligence. The routine, rule-based tasks and basic operations that employees find repetitive and mundane could potentially be ideal for RPA implementation. RPA software applications are commonly referred to as “digital FTEs” or “human proxies” because they can work and interact with existing systems as a person would.
Providers of the new software say it usually costs about one-third of an offshore employee or one-fifth of an onshore employee, but it can work nonstop, with no human errors — if programmed correctly.

With numbers like that, it is no wonder RPA has caught the attention of shared services organizations, which are designed to ultimately be cost savers and to provide consistent back-office processes and business support.
Source: Gartner
For businesses diving into automation or setting aside funds for it, it’s really important to understand what Robotic Process Automation (RPA) is all about, how to put it into action, what benefits it can bring, and the obstacles you’ll face along the way. It’s key to have a solid plan to tackle those challenges head-on.
To gain a better rationale and understanding of these finding from Gartner and Blueprint, I picked our subject matter experts’ brains.

Meet our experts:

Jyothsna Chandran,
Director – Digital Engineering

Rajalakshmi Sivaramakrishnan,
Solution Lead – Technology offerings
This newsletter aims to cover:
- Finding automation readiness
- RPA implementation roadmap
- Transitioning to intelligent automation – Nice-to-have and Must-have factors
- RPA tools
- Dealing with technical debt in RPA
- Change management concepts
- Common challenges in RPA implementation and overcoming them
Keerthi: How to identify automation-readiness for an organization?
Jyothsna Chandran: Below are some key areas to be considered to identify the automation readiness of an organization. By examining these factors, organizations can gain insights into their readiness for automation and make informed decisions about implementing automation initiatives effectively.
Identifying the Right Processes for Automation: Not all processes are suitable for automation. Organizations must identify the right tasks and functions that can benefit from automation to make informed decisions. Look for tasks or processes that are rule-based, repetitive, and involve a high volume of transactions. Consider tasks requiring significant human effort but with clear rules and guidelines. These are often suitable candidates for automation.
Automation Maturity and Standardization of Processes: understand your organization’s current automation capabilities. Evaluate the level of automation adoption/ process standardization in various departments. Automation is more effective in standardized processes. Assess the level of standardization in the targeted processes to determine their suitability for automation.
Creating Your Automation Roadmap: With insights from the automation maturity assessment, it’s time to create your automation roadmap. Tailor your plan according to your organization’s unique needs and objectives. Set achievable milestones and timelines for automation implementation. Consider how each phase of automation aligns with your overall business strategy.
Prepare for roadblocks: Common roadblocks include employee resistance to change, concerns about job security, and technical complexities. The success of automation relies on your team’s readiness to embrace the changes. Offer comprehensive training programs to help employees adapt to new technologies and workflows.
Governance mechanisms: As part of governance mechanisms, evaluate leadership commitment. Assess technology infrastructure, security measures, & consider scalability.
- Ensure regulatory compliance
- Evaluate change readiness
- Conduct a cost-benefit analysis
- Set key performance indicators to measure success
Keerthi: What do you think are the key steps/processes to creating an RPA implementation roadmap
Jyothsna Chandran:
Before going into the process and key steps for an RPA roadmap, let us first understand the 4 axes of automation which consists of people, process, system and purpose.
When people have the right set of digital skills and by integrating people and operations, the process of innovation starts with automation.
Imagine new processes. What can be done differently now that there’s automation? What can be done that was never possible before? How can you launch businesses faster?
Transition from rule-based procedures to pattern-based process by implementing Machine Learning models on your available data. Automation helps by feeding data into these models and extracting insights from them. With continuous experimentation, you can enhance decision-making, making it more efficient and responsive to rapidly changing market conditions.
All the above advance an organization’s purpose of moving away from mundane to special.
Rajalakshmi Sivaramakrishnan:
Define Strategic Objectives: Clearly define the strategic goals of your RPA journey and ensure seamless alignment with your business strategy and vision.
Assess Current Processes: Businesses should identify and prioritize processes that are high-volume, low-complexity, stable, and standardized. Evaluation of benefits and risks, including potential savings and regulatory compliance, is crucial for a successful automation strategy.
Design your Solution: Creating a detailed blueprint of how the software robots will interact with the applications, systems, and data sources involved in the process is another crucial step.
Develop a Proof of Concept (PoC): A well-established PoC in the RPA implementation roadmap offers a practical and strategic approach to validate, refine, and gain valuable insights. This stage offers a foundation for successful and scalable automation journey.
Optimize and Scale: This phase involves addressing issues, errors, and bottlenecks, seeking opportunities for improvement, and updating for sustained quality. Also, consider scaling your solution to other processes, departments, or locations if proven beneficial.
Keerthi: Transitioning from simple rule-based business tasks automation to intelligent automation – Can you briefly speak about the “Nice-to-have” and “Must-have” factors?
72% of organizations reported that their RPA estates contain mostly simple, rule-based task automation with some intelligent automation – Blueprint Report
Rajalakshmi Sivaramakrishnan: Intelligent automation is a system that utilizes Machine learning (ML) and Artificial Intelligence (AI) to automate routine tasks with enhanced accuracy.
Nice-to-have Factors:
- Inclusion of chatbots and virtual assistants to enhance user engagement.
- Integrating systems that possess adaptive learning functionalities to promote continuous enhancement.
- Provision for customization and flexibility enables adaptation to specific business requirements, accommodating diverse and changing demands in the business environment.
- Integration of different technologies and platforms to establish a unified and efficient digital infrastructure.
Must-have Factors:
- Implementing advanced analytics and machine learning for data analysis and adaptive learning.
- Integrating cognitive capabilities, such as natural language processing to enhance problem solving.
- Ability to scale automation solutions across diverse business functions and manage increased workloads.
- Implementing robust security measures to protect sensitive data and ensure compliance.
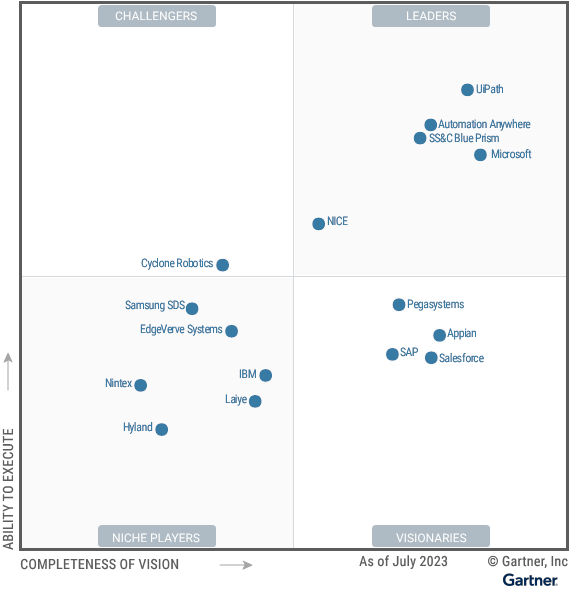
Additionally, Gartner’s Magic quadrant for RPA throws light on:



Keerthi: “In Blueprint’s 2022 research on the State of RPA, improving governance was the top objective organizations wanted to improve for their automation practice moving forward.”
What will be your tips to building an RPA CoE?
Jyothsna Chandran:
We can think of governance in 3 broad angles – people, process and technology.
People: What are the roles & responsibilities of your automation team? These include establishing resourcing needs, formal roles and responsibilities, and developing the necessary operations skills.
From a process perspective, how are you designing processes to govern and control automation while encouraging widespread adoption? Areas to think include right from defining a structure that guides everything from releases to supporting 3rd party automations to managing incidents.
On the technology side, how are you leveraging technology to enable and manage the program can be accomplished by employing capabilities to proactively identify, manage, and report on operational issues.
Self-sustaining and scalable RPA expertise team that makes automation capabilities available throughout the organization as a lever to deliver efficient business processes, increased business value and overall positive impact. Regardless of its task, a robot’s essential job is to make the company vision come true. To achieve this goal, it is advisable for the organization to build a Center of Excellence (CoE), that enables RPA effectively into the organization and to ensure knowledge and resources across future deployments.
Creating a formal CoE is an important step to ensure an organization’s automation potential.
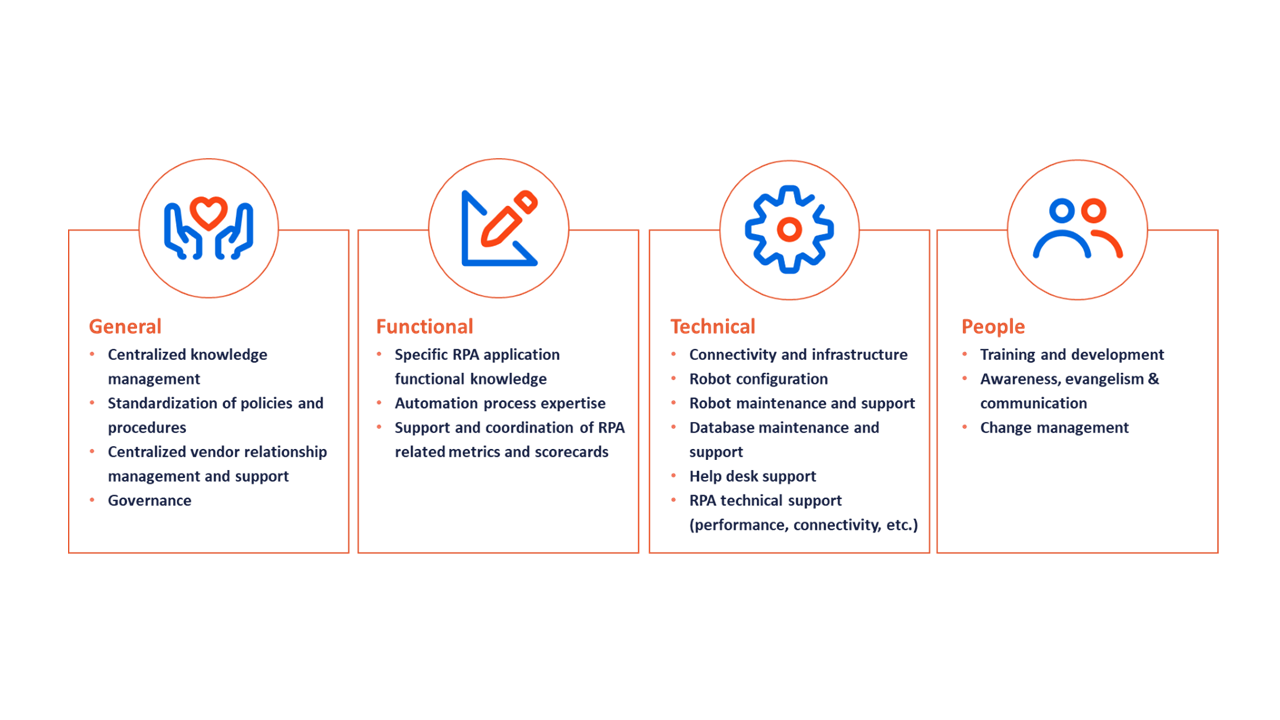
Building an RPA CoE requires more than just a generic IT team. It requires a team that will support that process from implementation, management, and scaling automation company wide.
50% of surveyed organizations reported they already have an RPA Center of Excellence and 39% confessed while they don’t have one currently, they are planning to implement one – Blueprint Report
Step 1: Build the skills and capacity for RPA: At the core of your CoE is the Robotic Operating Team which consists of a set of clearly defined roles and responsibilities. The team is in charge of implementing and managing the automation quickly, efficiently, and safely. Important roles include a Sponsor, Champion, Change Manager, Business Analyst(s), RPA Solution Architect, RPA Developer(s), RPA Infra Engineers.
Step 2: Effective Governance Model: The governance process oversees assessing RPA opportunities and prioritizing automation activities. It establishes the templates and guidelines for assessment, design, development, deployment, demand pipeline, and change management and risk management. The governance helps assign roles to ensure strong collaboration and communication between business, IT, and compliance teams. The governance process also outlines the performance and productivity metrics.
Step 3: Enable CoE and prepare for scale-up:
- Start with one project – but plan for many
- Embed learning along the way
- Manage the complexity of technical debt
- Expect the role and operating model of the CoE to evolve over time
- Guide the CoE to explore hyper automation
Keerthi: “Microsoft Power Automate is the most commonly used RPA platform (60%)” – Blueprint report. Your thoughts on this.
Jyothsna Chandran:
Microsoft Power Automate is not typically classified as a traditional Robotic Process Automation (RPA) tool but is considered more of an automation platform with a broader focus on workflow automation, business process automation, and integration capabilities.
The most common reason cited by organizations that use multiple RPA tools is due to compatibility with enterprise architecture (27%) – Blueprint Report
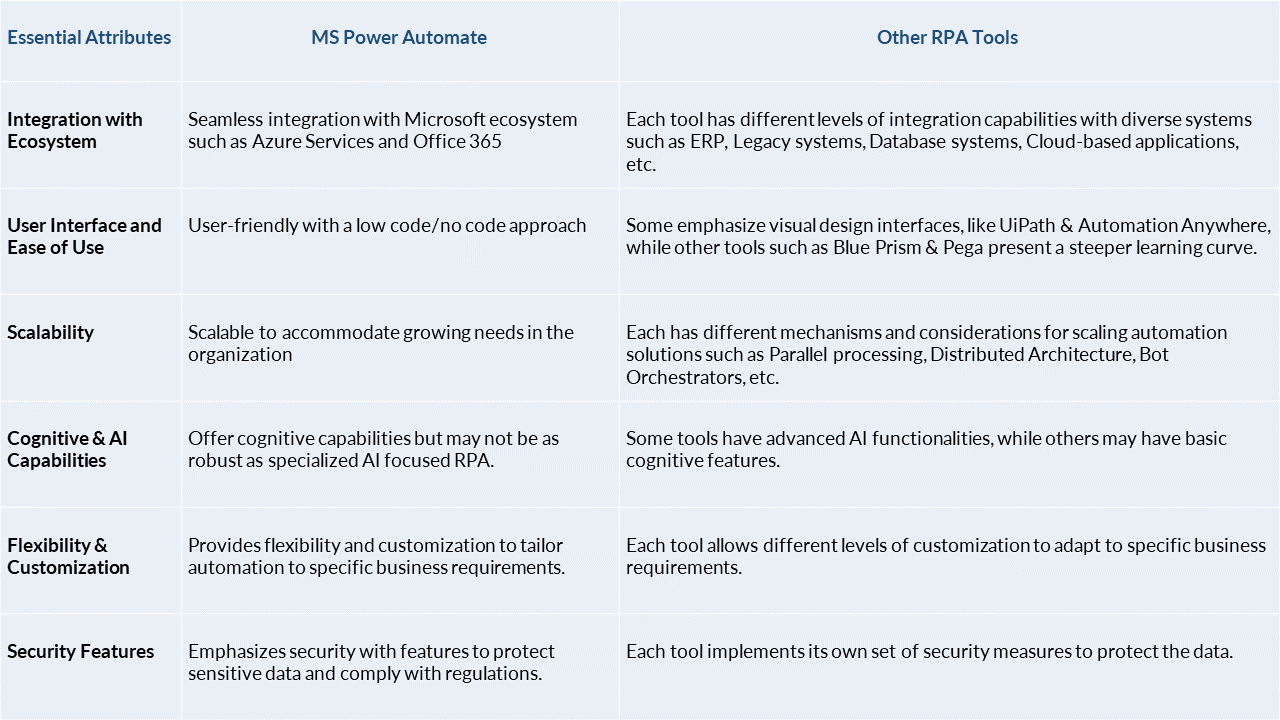
In a comparison between Microsoft Power Automate and other dedicated RPA tools, such as UiPath, Blue Prism, or Automation Anywhere, there are several factors to consider.
Rajalakshmi Sivaramakrishnan:
MS Power Automate Vs Other RPA Tools:
Keerthi: How should organizations go about understanding and dealing with technical debt in RPA/Intelligent automation?
Jyothsna Chandran:
Even prior to the rise of robots, enterprise architects and the technical community have been concerned about technical debt. Now the concern is accelerated. Technical debt is caused by the business driving faster adoption of more and more features or in this case, bots without considering the possibility of redundant, unused, unaccounted, or improper code (in the form of bot artefacts) clogging up the enterprise.
Having a standardized, enterprise-wide strategy for RPA and Intelligent Automation implementation is key for making smart investments to reduce technical debt rather than increase it.
For a CoE to help an organization achieve its RPA goals, it must also manage the technology’s underlying complexities. This means that it’s up to members of the CoE to control the design, source code, manage versioning challenges, and the dynamic credentials for bots to access existing systems.
Keerthi: Your thoughts on – Change Management: A Key Factor in RPA Implementation Success
Jyothsna Chandran:
Change management is a critical factor in the success of RPA implementation. RPA initiatives often bring about significant changes in processes, roles, and organizational dynamics. Managing these changes is essential to maximize the benefits of automation.
Here are some key aspects highlighting the importance of change management in RPA implementation:
Employee Engagement: Change management involves engaging employees at all levels of the organization. Ensuring that employees understand the purpose of RPA, how it will impact their roles, and how it aligns with organizational goals helps build support and reduces resistance.
Communication Strategy: Employees should be informed about the RPA initiative, its objectives, and the benefits it brings. Regular updates and open communication channels help manage expectations and address concerns.
Training Programs: Providing adequate training is essential for employees to adapt to new technologies and processes. Training programs should be designed to empower employees with the skills needed to work alongside RPA bots and understand their changed responsibilities.
Change Champions: Identifying and empowering change champions within the organization can significantly influence the success of RPA implementation. These individuals can serve as advocates, helping to disseminate information, address concerns, and inspire others.
Setting Realistic Expectations: Managing expectations is crucial for RPA success. Clearly communicating what RPA can and cannot achieve helps avoid unrealistic expectations.
Leadership Support: Leadership plays a pivotal role in change management. Visible support and commitment from top leadership create a positive tone for the entire organization. Leaders should communicate the strategic importance of RPA and actively participate in the change process.
Measuring and Celebrating Success: Last but not least, establish KPIs to measure the success of RPA implementation. Reinforce the positive impact of the automation initiative.
Organizations that invest time and resources in addressing the human side of the change equation are more likely to see successful RPA adoption and long-term benefits.
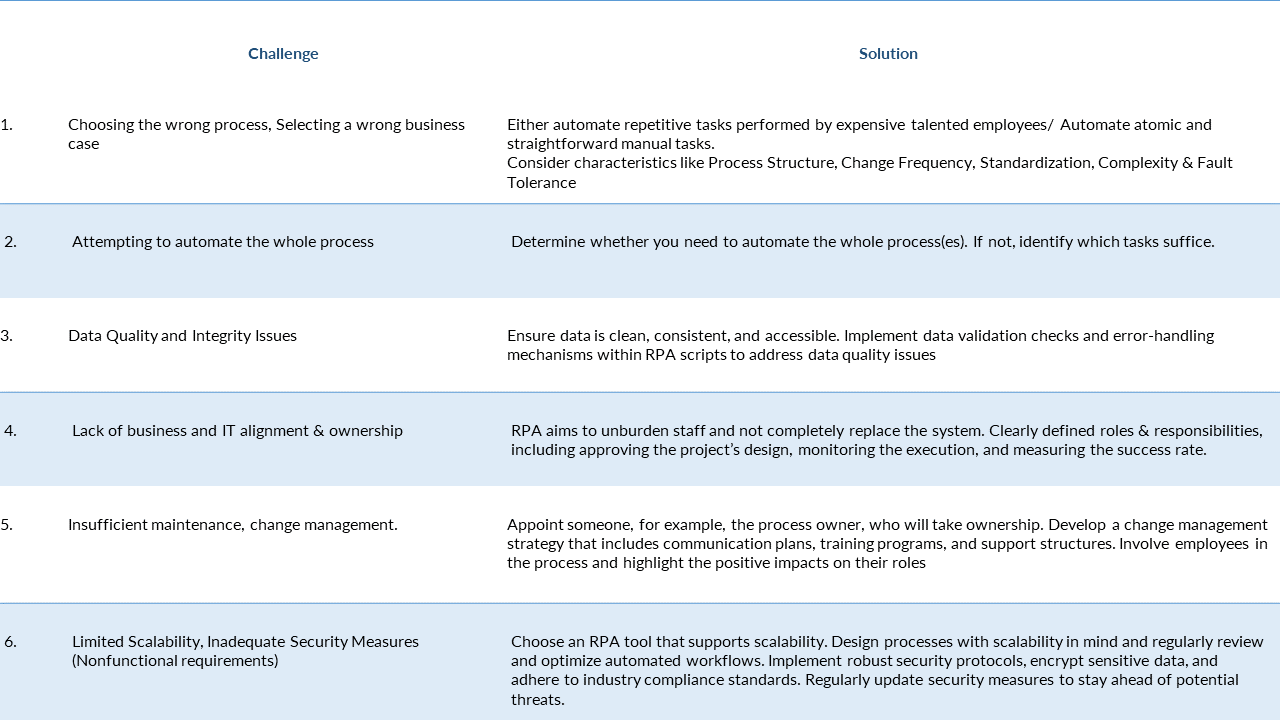
Keerthi: Common pitfalls and challenges in RPA implementation & how to overcome them?
Jyothsna Chandran:
By anticipating and addressing the common pitfalls, organizations can increase the likelihood of a successful RPA implementation and realize the full benefits of automation. Regularly reassessing and optimizing processes will contribute to sustained success over the long term.
Most organizations (41%) set up their RPA practice with external parties, and a significant percentage (34%) reported they used a combination of internal and external resources to implement automation – Blueprint Report
Read more on the subject:
Thanks for reading! We’re excited about delving deeper into RPA and implementation in our future editions.
If you like our content, show us your support by – Subscribing to our quarterly newsletter, Sound bytes here. and by sharing this article with your team. Your support means the world to us!

