With 2024 lurking around the corner, it’s time to think big, pioneer new technologies, and rapidly deliver differentiated digital capabilities and revenues for your business.
Though AI is already topping the headlines and ruling a majority of businesses, it’s not the only technology trend that will capture the global market and help you drive value and customer expectations.
In this LinkedIn newsletter of Season 2 Edition 6, we have delved deeper into Gartner’s report, ‘Top Strategic Technology Trends 2024’*, analyzed the trends with the help of our technical wizards, and are here to share the insights with you to identify emerging technologies, build robust strategies and drive value for both internal and external stakeholders.
Hello readers,
I am Ameena Siddiqa, Marketing Strategist at Zuci Systems. To gain deeper insights into the aforementioned report, I tapped into the expertise of our technology enthusiasts and experts, Prasanna Venkatesh PK , Vice President, Digital Engineering, and Clarence Fernando , Delivery Manager, Digital Engineering.
Let’s delve into the topic!
1. Platform Engineering
Gartner predicts that 80% of software engineering organizations will establish platform teams as internal providers of reusable services, components, and tools for application delivery.
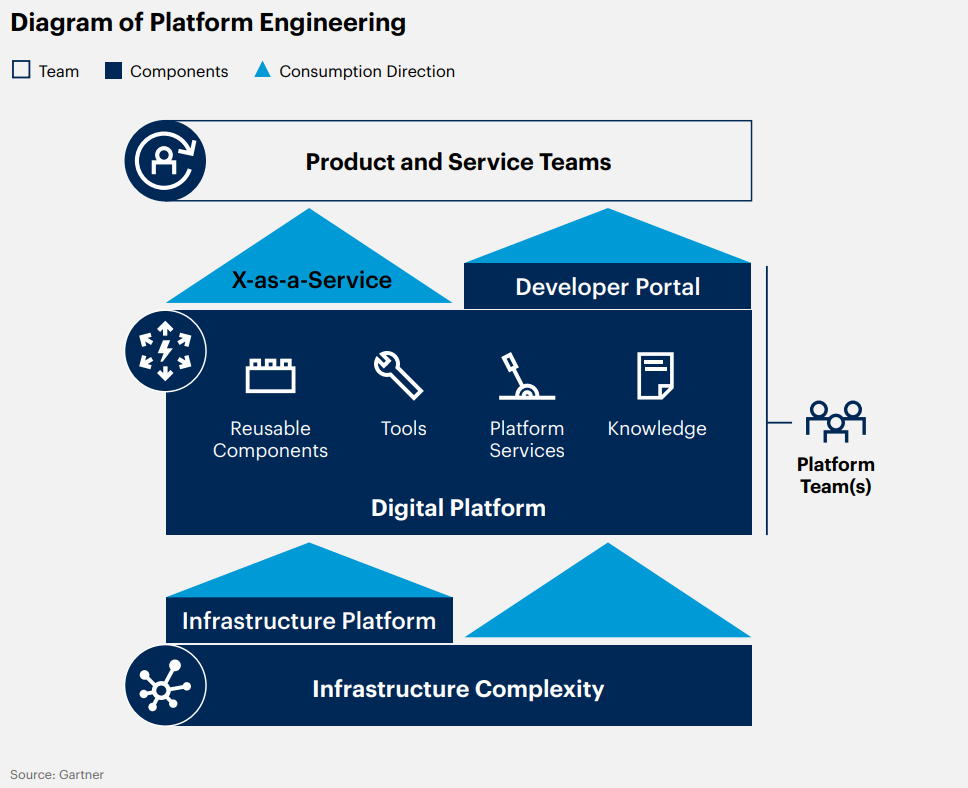
Ameena: How does platform engineering enhance the developer’s experience and accelerate the delivery of business value?
Prasanna V: Platform engineering holds the promise of resolving the core challenge of collaboration between software developers and the operations team. By incorporating reusable tools and self-service capabilities, and automating infrastructure operations, this technological approach enhances both the developer experience and productivity. Let’s take a look at some of the hard-to-miss benefits of Platform Engineering;
1. Moving beyond: DevOps and DevSecOps frameworks
Derived from the groundwork laid by DevOps and DevSecOps frameworks, platform engineering places a strong emphasis on improving developer productivity. It goes beyond collaboration and security integration to streamline workflows, automate tasks, and create an environment where developers can focus on writing code and delivering value.
2. Empowering Developers for Strategic Focus
As an essential enabler, Platform Engineering liberates developers from their cognitive load and other intricacies of infrastructure management. This shift allows developers to redirect their attention and energy toward solving complex business problems rather than being bogged down by the operational aspects of their applications. This, in turn, paves the way for enhanced overall productivity and innovation within the software development lifecycle.
3. Azure and AWS: Pioneers in Platform Engineering Support
Recognizing how vital Platform Engineering is, major cloud service providers like Azure and AWS have proactively incorporated it into their strategic frameworks. They offer robust tools and resources that make it easier for the end users to embrace Platform Engineering seamlessly.
In a nutshell, platform engineering lays the groundwork for a future-ready infrastructure that adapts seamlessly to changing business requirements, acts as a catalyst for higher velocity development, and ensures sustained success in the dynamic world of software development.
Ameena: How can mid and enterprise-level organizations get the most out of Platform Engineering in 2024?
Prasanna V: The successful adoption of Platform Engineering involves strategic decision-making, a product-centric mindset, and a commitment to continuous improvement through active collaboration and feedback loops, among other key approaches. Let’s delve into notable strategies that will help organizations in making the most out of this technology:
1. Strategic Decision-Making for Platform Adoption
The establishment of Platform Engineering demands a strategic decision by organizations to recognize and leverage its potential. It requires end-to-end evaluation of the existing landscape and an understanding of how Platform Engineering aligns with the broader organizational goals.
2. Product-Like Approach to Platform Setup
To extract maximum value from Platform Engineering, organizations should adopt a “product-like” mentality when establishing platforms. This involves considering the platform as a product in itself, with an emphasis on user experience, collaboration, and iterative development.
3. Templating for Technology and Delivery Needs
An essential step in effective Platform Engineering is the templatization of platforms based on specific technology requirements and end-delivery specifications. This plays a key role in promoting consistency and scalability across diverse projects.
4. End-Deliverable Centric Approach for Developer Empowerment
Focusing on end-deliverable requirements is pivotal for the success of Platform Engineering. This approach transforms the platform into a personalized solution, directly addressing the concerns of developers, and allowing them to concentrate on solving business problems rather than grappling with complex infrastructure intricacies.
5. Continuous Improvement Through Developer Feedback
Organizations should actively seek and implement feedback from the developer community on Platform Engineering tools and approaches. This ongoing feedback loop ensures that the platform evolves organically, staying responsive to the dynamic needs of software development.
In 2024, platform engineering will emerge as a dynamic and multifaceted discipline that profoundly influences the trajectory of IT.
Organizations adopting contemporary platform engineering practices find themselves well-equipped to navigate the intricate digital terrain, accelerate time-to-market, and provide exceptional user experience.
2. Sustainable Technology
Ameena: How can CIOs strategically align their technology initiatives with sustainability goals to ensure a measurable and positive impact? What key performance indicators (KPIs) should they prioritize in this context?
Prasanna V: CIOs can strategically align their sustainability goals by adopting a holistic approach that brings environmental considerations and technology goals on the same page. For a tangible and positive effect, CIOs should consider implementing the following strategies.
1. Data Center Efficiency: Optimize data center efficiency to reduce energy consumption. Tap into advanced cooling technologies, virtualization, and energy-efficient hardware to enhance overall data center sustainability.
2. Integrated Sustainability Strategy: Build a robust sustainability strategy that aligns with the overall business goals. Ensure that technology initiatives are integrated into this broader sustainability framework.
3. Renewable Energy Adoption: Prioritize the use of renewable energy sources for data centers and other technology infrastructure. Shifting towards cleaner energy supports sustainability goals and reduces the carbon footprint.
4. Measurable Metrics and Reporting: Define key performance indicators (KPIs) to measure the impact of technology initiatives on sustainability. Metrics may include energy consumption, carbon emissions, waste reduction, and the overall environmental footprint.
Continuous Improvement: Establish a system for continuous improvement by regularly reviewing and updating sustainability initiatives. Incorporate feedback from stakeholders and adapt strategies based on changing technology landscapes and environmental considerations.
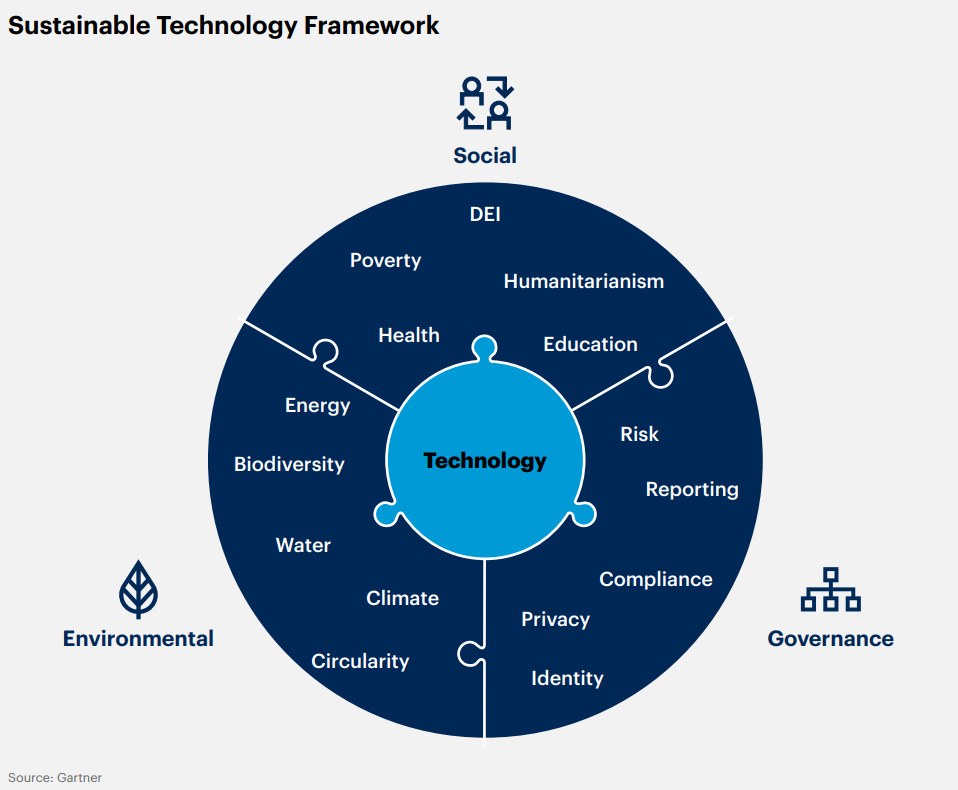
Here are the Key Performance Indicators (KPIs) for measuring the impact of technology initiatives on sustainability:
1. Energy Efficiency Ratio (EER): Measure the energy efficiency of data centers and IT infrastructure.
2. Carbon Intensity: Calculate the amount of carbon emissions produced per unit of output to assess the environmental impact.
3. Renewable Energy Usage: Track the percentage of energy sourced from renewable sources.
4. Waste Reduction: Monitor and reduce electronic waste through responsible disposal and recycling programs.
5. Smart Commute Initiatives: Evaluate options of Remote work initiatives on non-collaborative and support tasks, encourage staying within 3 miles of work location, using public transport, electric vehicles, and car-pool to cut down the emissions.
6. Supplier Sustainability Ratings: Assess and report on the sustainability practices of technology suppliers and partners. Calculating the Supply Chain Miles would help in managing sustainability initiatives of procurement and distribution.
Prioritizing sustainability technology is not just about meeting environmental goals. It’s a strategic imperative that impacts brand image, financial performance, talent engagement, and long-term business resilience. CIOs can drive meaningful progress toward aligning technology initiatives with sustainability goals and ensuring a positive and measurable impact.
Ameena: How can organizations extend their Sustainable Technology practices across geographical boundaries and navigate regional challenges?
Prasanna V: Extending sustainable technology practices across geographical boundaries while navigating regional challenges is an arduous task. Some of the tested approaches that can help organizations effortlessly mitigate these challenges are:
1. Global Sustainability Framework
Plan and adopt global standards and standards required as per industry and region to make a compelling case for sustainability framework, define roadmaps, and measure progress. Some of the notable ESG frameworks include GRI, SASB, ISO 14001m, EU CSRD (ESRS), UNFSS, IIRC, TCFD, ISSB (IFRS), CDP, and B Corp.
2. Regional Customizations
Customize sustainable technology practices to fit cultural practices, environmental regulations, and technology practices to fit each region’s unique context to ensure relevance and effectiveness.
3. Regulatory Compliance Management
Stay updated about environmental regulations in each region and integrate compliance requirements into sustainability strategies to mitigate legal risks and adhere to local laws.
4. Technology Adaptation
Adapt technology solutions to the varying infrastructure and resource availability in different regions. Explore scalable and modular solutions that can be modified based on regional requirements.
5. Data-Driven Decision-Making
Implement data analytics to assess the environmental impact of operations in each region. Tap into data-driven insights to identify areas for improvement, optimize resource usage, and measure the effectiveness of sustainable technology initiatives.
6. Continuous Monitoring and Reporting
Build a robust system for continuous monitoring of sustainability performance in each region. Regularly update internal and external stakeholders to portray the organization’s commitment to transparency and accountability.
These are some of the prominent strategies that can help enterprises spread eco-friendly tech practices worldwide and handle local issues well and go a long way in working together for a healthier planet.
Moving on to Clarence to get his insights on the next technology trend on our list.
3. Democratized Generative AI
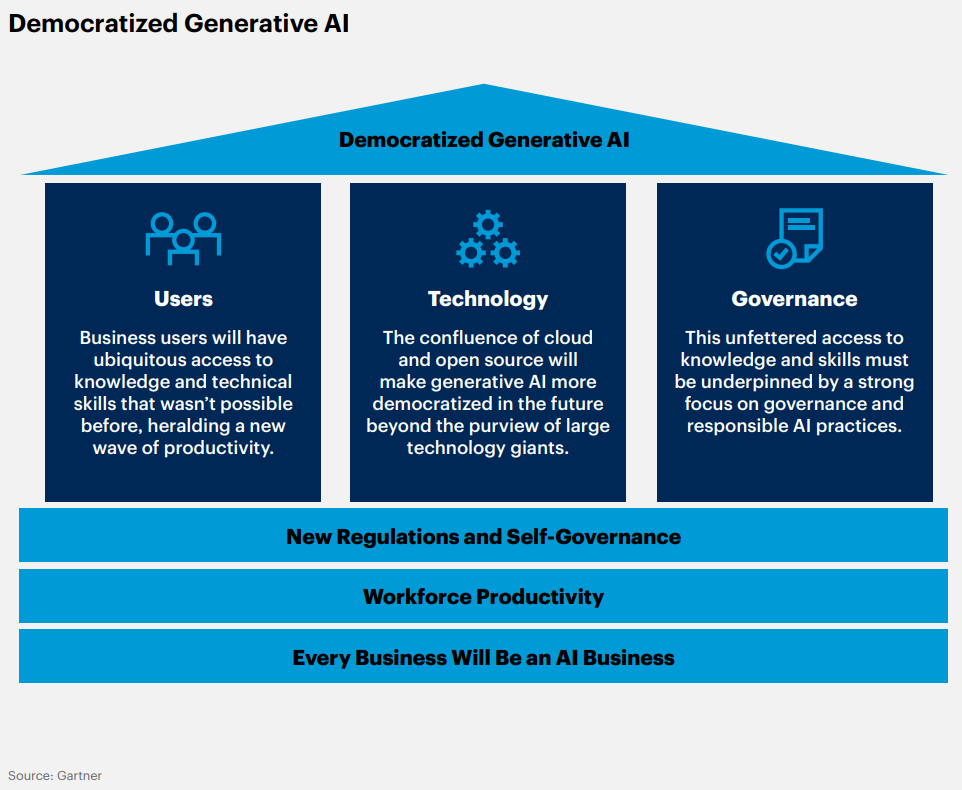
Ameena: How can businesses strategically leverage generative AI APIs and models to gain a competitive edge in their respective industries?
Clarence: The widespread accessibility of generative AI technology has the power to revolutionize industries. It helps businesses get innovative, automate tasks, and streamline processes, paving the way for exciting chances to better connect with customers and enhance product development. Here are some examples;
1. Personalized Customer Experience
Chatbots powered by AI models can engage with customers, provide personalized recommendations, and solutions, and enhance overall customer satisfaction.
2. Product Design and Prototyping
AI models can generate design options based on specific criteria set by the users and help businesses explore a wide range of possibilities efficiently.
3. Automated Data Analysis
AI models can process large datasets, extract meaningful insights, and generate reports, enabling faster and more informed decision-making.
4. Natural Language Processing (NLP) Applications
Generative AI APIs for natural language processing applications can enhance communication channels, automate responses in customer support, and enable sentiment analysis for a better understanding of customer feedback.
5. Augmented Reality (AR) and Virtual Reality (VR) Experiences
Integrating generative AI into AR and VR experiences can help in generating content within these immersive environments, providing users with personalized and interactive experiences.
6. Cybersecurity Threat Detection
Generative AI models for cybersecurity threat detection can analyze network patterns, detect anomalies, and generate alerts for potential security threats, enhancing overall cybersecurity measures.
7. Financial Forecasting
AI models can analyze financial data, generate predictive models, and assist businesses in making informed financial decisions.
Ameena: What potential obstacles or limitations might enterprises face in adopting generative AI on such a widespread scale, considering the current landscape and technological constraints?
Clarence: As companies strive to make the most of this technology, they often overlook its potential downsides. The widespread adoption of generative AI by enterprises is accompanied by several potential obstacles and limitations. Some of the hard-to-overlook constraints are;
1. Data Privacy and Security Concerns
Widespread adoption of generative AI involves processing large volumes of sensitive data. Enterprises may face challenges in safeguarding against unauthorized access and breaches.
2. Ethical Use and Bias
The use of generative AI raises ethical concerns, especially in generating content or making decisions autonomously. Understanding how decisions are made and who is responsible for potential consequences becomes challenging.
3. Interpretability and Explainability
Generative AI models, particularly deep learning models, can be complex and challenging to interpret. Lack of transparency in decision-making processes may hinder trust and understanding, especially in industries with stringent regulatory requirements.
4. Resource Intensiveness
Training and deploying generative AI models requires substantial computing power and storage. Small and medium-sized enterprises may face challenges in investing in infrastructure and resources.
5. Lack of Skilled Talent
The demand for skilled professionals in generative AI often outstrips the available talent pool. Enterprises may face challenges in recruiting and retaining experts who can effectively develop, implement, and manage generative AI systems.
Briefly, the challenges and limitations that come with the extensive adoption of generative AI emphasize the importance of thoughtful deliberation, ethical deployment, and continuous efforts to tackle technical, societal, and regulatory hurdles in the dynamic landscape.
Every organization has unique goals and objectives, and the impact of each technology trend varies from one organization to the other. As a head start, evaluate which of these trends brings opportunities and risks aligned with your organization’s strategic direction before drafting out the roadmap. This will help you achieve reliable and sustainable business growth and outshine your competition.
Thank you for delving into our expert’s insights. We actively explore trending reports from reputable names like Gartner, Forrester, McKinsey, etc., We analyze them with the help of our technology experts and share our insights to achieve digital excellence. Tap on the subscribe button to read our upcoming newsletter editions.
Resources:
